Smoking May Aggravate Varicose Vein Symptoms?
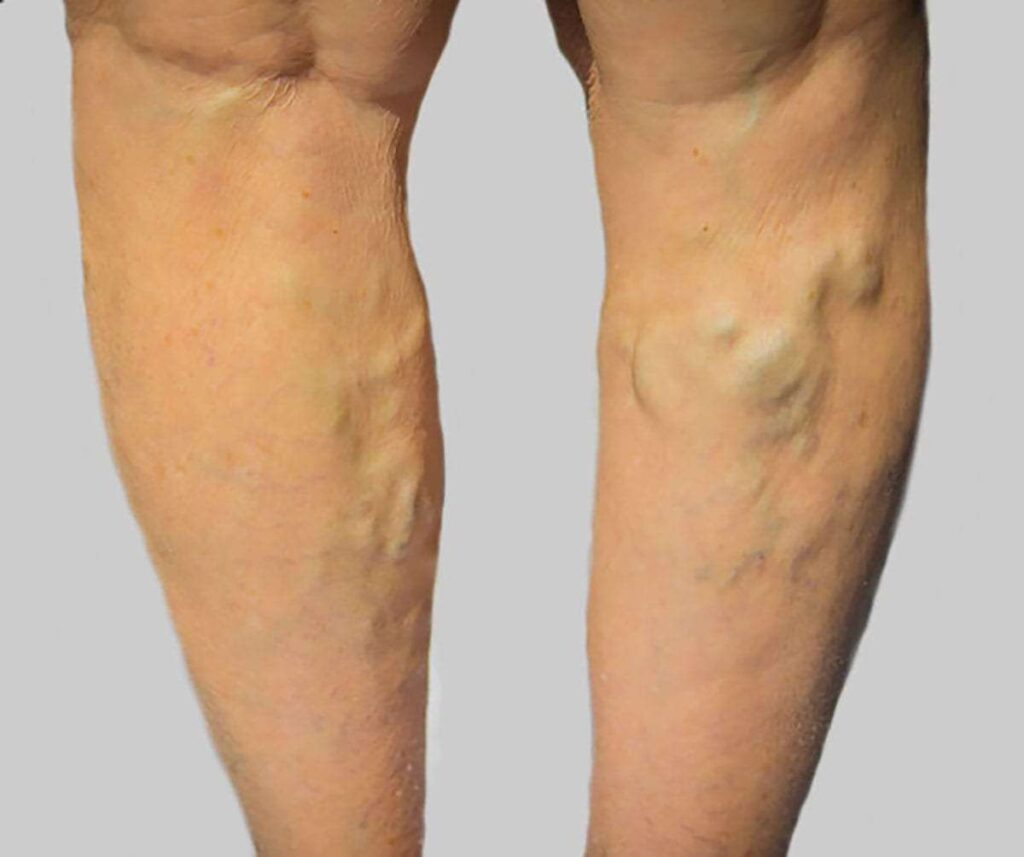
Varicose veins are twisted, enlarged veins often found on the legs, resulting from faulty valves that allow blood to pool instead of flowing efficiently back to the heart. They can cause symptoms like swelling, aching, and discomfort. While several factors contribute to the development and worsening of varicose veins—such as age, genetics, pregnancy, and prolonged standing—smoking is another significant risk factor that can aggravate this condition. Smoking is notorious for negatively affecting overall vascular health, and its impact on varicose veins is no exception. In this article, we will explore the ways in which smoking may exacerbate varicose vein symptoms, the mechanisms behind it, and strategies for managing varicose veins effectively.Smoking May Aggravate Varicose Vein Symptoms?

1. How Smoking Impacts Vein Health
Smoking impacts vein health in several harmful ways, directly contributing to the worsening of varicose veins. Cigarettes contain thousands of chemicals, many of which are toxic and detrimental to cardiovascular health. The main ways in which smoking affects vein health include:
- Damage to Blood Vessels: Smoking causes inflammation and oxidative stress, leading to the weakening and damage of the vein walls. This is particularly problematic for people with varicose veins because the veins are already weakened, and any additional strain can lead to worsening symptoms.
- Restricted Blood Flow: Nicotine, one of the primary chemicals in cigarettes, causes blood vessels to constrict, reducing blood flow. In people with varicose veins, this reduced blood flow can exacerbate the pooling of blood, leading to increased pressure within the veins.
- Impaired Oxygen Supply: Smoking reduces the oxygen content in the blood, which means that the tissues and muscles surrounding varicose veins may not receive adequate oxygen. This lack of oxygen further weakens the vein walls and impairs their ability to function properly.
2. Smoking and Valve Dysfunction in Veins
Varicose veins occur due to faulty valves within the veins that fail to keep blood flowing in one direction—toward the heart. Instead, these damaged valves allow blood to flow backward and pool in the veins, causing them to swell. Smoking plays a significant role in this valve dysfunction:
- Increased Pressure on Valves: Smoking increases blood pressure, and elevated blood pressure in the legs puts additional strain on the already weakened valves. Over time, this strain leads to further valve damage, which exacerbates the pooling of blood in the veins.
- Inflammation of Vein Valves: The chemicals in cigarette smoke cause chronic inflammation throughout the vascular system, including the valves in the veins. This inflammation damages the valve tissues, reducing their efficiency in controlling blood flow.
3. Smoking as a Contributing Factor to Inflammation
Inflammation is a key factor in the development and progression of varicose veins, and smoking directly contributes to increased inflammation in the body. When you smoke, the chemicals in cigarettes—such as nicotine and tar—enter the bloodstream and trigger an inflammatory response. This inflammation affects not only the lungs and arteries but also the veins.
- Systemic Inflammation: Systemic inflammation makes the veins more prone to damage and dysfunction. Chronic inflammation leads to vein wall thickening, making it harder for blood to flow smoothly. In varicose veins, this can lead to a worsening of symptoms, such as swelling, discomfort, and increased pain.
- Worsened Symptoms: The inflammation caused by smoking leads to increased fluid leakage from veins into surrounding tissues, resulting in leg swelling (edema). This can significantly increase the discomfort experienced by individuals with varicose veins.
4. Blood Thickening and Clot Formation
Another way smoking aggravates varicose veins is by increasing the risk of blood clot formation. Smoking makes the blood thicker and more prone to clotting. This can have serious implications for those with varicose veins:
- Risk of Superficial Thrombophlebitis: People with varicose veins are at an increased risk of developing superficial thrombophlebitis, which is an inflammation of a vein just below the skin’s surface, often accompanied by a clot. Smoking increases the risk of clot formation, which in turn increases the risk of thrombophlebitis and other complications related to varicose veins.
- Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): In some cases, varicose veins and smoking combined can increase the risk of deep vein thrombosis (DVT), a more serious condition where a blood clot forms in a deep vein, typically in the legs. DVT can cause pain, swelling, and even life-threatening complications if the clot dislodges and travels to the lungs (pulmonary embolism).

5. Reduced Healing Capacity
Smoking impairs the body’s natural healing capacity, which affects the management and treatment of varicose veins. When veins are weakened and swollen, the body needs to repair the vein walls and surrounding tissues. Smoking interferes with this healing process in several ways:
- Reduced Collagen Production: Collagen is an essential protein for maintaining the elasticity and integrity of vein walls. Smoking reduces the production of collagen, making the veins weaker and more susceptible to damage. As a result, the varicose veins may become larger, more painful, and more prone to complications over time.
- Delayed Wound Healing: If you develop skin ulcers or other skin issues due to varicose veins, smoking can delay the healing of these wounds. This is because smoking reduces blood flow and oxygen delivery, both of which are critical for the healing process. Chronic wounds or ulcers are common complications of severe varicose veins and can be difficult to treat in smokers.
6. Symptoms of Varicose Veins Worsened by Smoking
Smoking can make several symptoms of varicose veins worse:
- Increased Pain: The pain associated with varicose veins can be significantly aggravated by smoking due to reduced blood flow, inflammation, and oxygen deficiency in the affected area. This can lead to more frequent and intense discomfort, particularly after standing for long periods.
- Swelling and Leg Heaviness: Smoking causes veins to constrict and reduces circulation, leading to increased swelling in the legs. The sense of heaviness often felt in the legs by those with varicose veins becomes even more pronounced with smoking.
- Muscle Cramps: Poor circulation from smoking can increase the occurrence of muscle cramps in people with varicose veins. Cramps, especially those occurring at night, are often linked to insufficient oxygen supply to the muscles—a problem worsened by smoking.
7. Long-Term Effects of Smoking on Varicose Veins
The long-term effects of smoking on individuals with varicose veins are significant:
- Progression of Varicose Veins: Smoking accelerates the progression of varicose veins by continually damaging vein walls, increasing blood pressure, and promoting inflammation. This means that varicose veins may become larger, more painful, and spread to new areas of the legs.
- Increased Risk of Complications: Smokers with varicose veins are more likely to experience complications such as leg ulcers, skin changes, and venous insufficiency, which may require medical intervention. The risk of developing dangerous blood clots is also increased for smokers.
- Poor Treatment Outcomes: Smoking can also reduce the effectiveness of medical treatments for varicose veins, such as sclerotherapy or laser treatments, because of impaired healing and reduced vascular health. It is often recommended that patients quit smoking before undergoing vein treatments to maximize the likelihood of success.
8. Benefits of Quitting Smoking for Varicose Veins
Quitting smoking can have numerous positive effects on the management and treatment of varicose veins:
- Improved Circulation: Once you stop smoking, circulation begins to improve. With better blood flow, the symptoms of varicose veins, such as swelling, heaviness, and cramping, may start to diminish.
- Reduced Inflammation: Quitting smoking reduces inflammation in the body, which can help alleviate the discomfort associated with varicose veins. Reduced inflammation means that vein valves can work more efficiently, reducing the pooling of blood.
- Better Healing: Quitting smoking allows the body to heal more effectively. If you require treatment for varicose veins, your body will respond better, and the likelihood of successful treatment outcomes will increase.
9. Strategies for Managing Varicose Veins If You Smoke
If you are struggling with varicose veins and are a smoker, there are several strategies you can use to manage your symptoms effectively:
- Quit Smoking: The most important step is to quit smoking. Although this can be challenging, the benefits for your vascular health—and your overall well-being—are substantial. Seek support from smoking cessation programs, healthcare professionals, or nicotine replacement therapies to help you quit.
- Wear Compression Stockings: Compression stockings help improve circulation in the legs and reduce symptoms of varicose veins, such as swelling and discomfort. They can be especially helpful for smokers, as they provide an additional boost to circulation.
- Stay Active: Exercise is vital for improving circulation and maintaining healthy veins. Activities such as walking, swimming, or cycling are particularly beneficial. Avoid prolonged sitting or standing, as this can exacerbate varicose veins.
- Healthy Diet: A diet rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals can help support vascular health. Foods high in vitamins C and E can promote healthy veins and reduce inflammation, which is important for counteracting the negative effects of smoking.
Conclusion
Smoking significantly aggravates the symptoms of varicose veins by reducing blood flow, increasing inflammation, damaging vein valves, and impairing the body’s ability to heal. People who smoke are more likely to experience worsened symptoms, a faster progression of their condition, and an increased risk of complications like ulcers and blood clots.
The best approach for managing varicose veins is to quit smoking, which can drastically improve vascular health and reduce symptoms. In addition to quitting smoking, managing varicose veins through lifestyle changes such as wearing compression stockings, staying active, and eating a healthy diet can further improve symptoms and promote healthier veins.
Quitting smoking is not just about improving the appearance of varicose veins; it is about enhancing your overall vascular health, improving your quality of life, and reducing the risk of serious complications. Taking steps to quit today can make a significant difference in managing varicose veins and ensuring a healthier future.
For Purchase Product Of Varicose Veins Click Here



