Visible Signs and Symptoms of Varicose Veins
Varicose veins are a widespread condition, especially in adults, where veins become swollen, twisted, and enlarged. They occur when valves in the veins fail to function properly, causing blood to pool and veins to enlarge, typically in the legs. While varicose veins are often viewed as a cosmetic issue, they can cause discomfort and, in severe cases, lead to complications such as skin ulcers or deep vein thrombosis.Discover the most common visible signs and symptoms of varicose veins, from bulging veins to skin discoloration. Learn how to recognize and manage this common condition.
This article explores the most common visible signs and symptoms of varicose veins, how they develop, and answers frequently asked questions to help you better understand this condition.
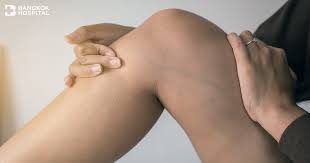
What are Varicose Veins?
Varicose veins develop when the veins, usually in the legs, struggle to circulate blood back to the heart. This inefficiency occurs because of faulty valves in the veins that allow blood to flow backward and pool in the veins, causing them to swell. Over time, the veins stretch and bulge, creating visible signs on the skin and leading to various symptoms.
Varicose veins can affect anyone, but they are more common in women, older adults, and individuals with a family history of the condition. Factors like pregnancy, obesity, standing for long periods, and hormonal changes can increase the risk of developing varicose veins.
Visible Signs and Symptoms of Varicose Veins
1. Enlarged, Twisted, and Bulging Veins
The most easily recognizable sign of varicose veins is the visible swelling of veins. These veins typically appear:
- Twisted or bulging: They often have a rope-like appearance, twisting under the skin and bulging outwards.
- Dark blue or purple: Varicose veins are usually a dark color, which is due to the blood pooling in them.
This characteristic appearance is most commonly seen in the legs, especially in the calves and thighs. In some cases, varicose veins may appear on other parts of the body, but they are primarily found in the lower extremities due to gravity and the body’s natural circulation patterns.
2. Leg Swelling (Edema)
Varicose veins can cause the swelling of the legs and ankles, especially after standing or sitting for long periods. This is due to blood pooling in the affected veins, causing pressure and fluid to leak into surrounding tissues.
- Localized swelling around the veins may be mild at first but can worsen over time, especially if varicose veins are left untreated.
- The swelling is often more noticeable by the end of the day or after prolonged inactivity, such as sitting at a desk or standing in one position for hours.
3. Skin Discoloration
As varicose veins worsen, they can cause changes in skin color, particularly in the areas surrounding the affected veins. Skin discoloration is often a sign of chronic venous insufficiency, where blood flow has been impaired for an extended period.
- Brownish or reddish patches may appear on the skin. This occurs due to hemosiderin deposition, where blood that leaks out of the veins breaks down and leaves iron deposits in the skin.
- Over time, the affected area can become darker, and the skin may harden (a condition known as lipodermatosclerosis).
4. Itching and Skin Irritation
Many people with varicose veins experience itching around the affected veins. This can occur due to the poor blood flow leading to skin irritation and dryness.
- Itchy, dry patches of skin are common and can be mistaken for other skin conditions such as eczema.
- Constant itching can lead to further irritation, redness, and inflammation of the skin, potentially causing sores or ulcers if scratched excessively.
5. Heavy or Achy Feeling in the Legs
One of the hallmark symptoms of varicose veins is a heavy or achy feeling in the legs. This sensation typically worsens at the end of the day or after long periods of standing or sitting.
- Leg fatigue: Many individuals describe a feeling of tiredness or fatigue in their legs, even after minimal activity.
- Worsening discomfort: The discomfort is often more intense after extended periods of inactivity, such as sitting for a long time, and may improve with movement or elevating the legs.
6. Throbbing or Burning Sensations
Varicose veins can cause a throbbing or burning sensation, particularly in the areas around the affected veins.
- Localized pain: This discomfort is often felt as a burning or throbbing in the legs, especially in areas where veins are particularly swollen.
- The pain can worsen during physical activity or after standing for long periods and may subside when the legs are elevated.
7. Muscle Cramps, Especially at Night
People with varicose veins often report leg cramps, particularly at night. These cramps may disrupt sleep and can be quite painful.
- Nocturnal cramps: These muscle spasms can wake individuals from sleep and cause sharp pain, especially in the calves.
- Relief: The pain may ease with leg movement or stretching, but the cramps can return regularly if varicose veins are not treated.
8. Skin Ulcers (Venous Ulcers)
In more severe cases of varicose veins, especially when combined with chronic venous insufficiency, skin ulcers may develop.
- Open sores: These ulcers typically form around the ankles and can be slow to heal. If left untreated, they can become infected and lead to further complications.
- Venous ulcers are usually a sign of advanced varicose veins and require medical treatment to prevent further tissue damage.
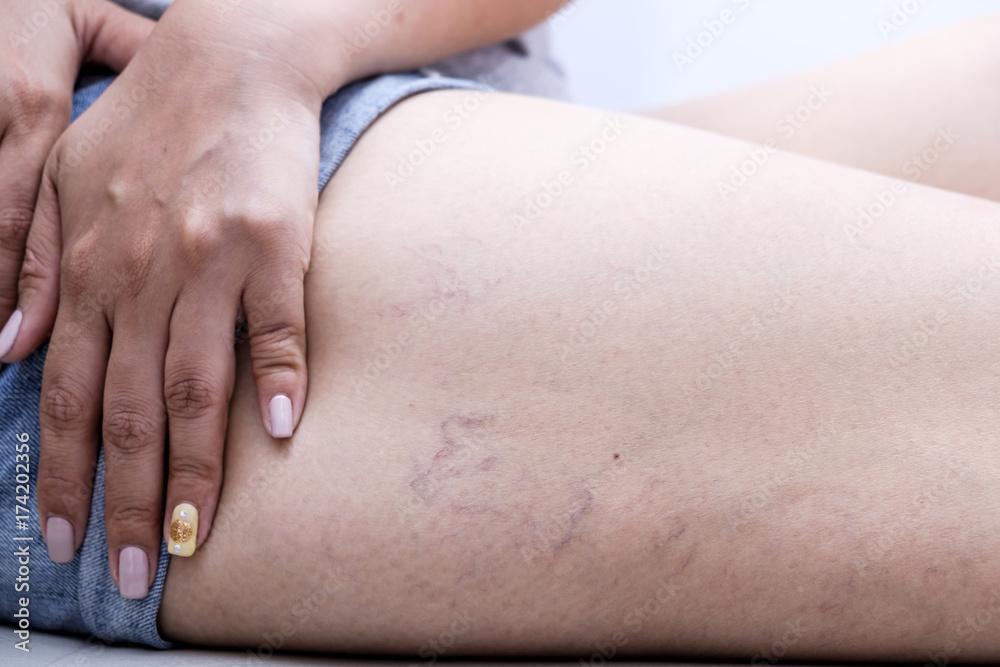
9. Spider Veins
While not as severe as varicose veins, spider veins are another visible symptom that may accompany the condition. Spider veins are smaller, red, purple, or blue veins that spread out like a web beneath the surface of the skin.
- Appearance: Spider veins are often found on the legs and face and are less prominent than varicose veins. However, they can cause discomfort and may indicate underlying venous issues.
10. Hardening of the Skin (Lipodermatosclerosis)
In advanced cases of varicose veins, the skin around the affected areas may harden due to chronic inflammation and poor circulation. This condition, known as lipodermatosclerosis, can make the skin feel tight, painful, and more prone to ulcers.
When to See a Doctor
While varicose veins are often viewed as a cosmetic issue, they can lead to more serious complications if left untreated. It’s important to consult a healthcare professional if you experience:
- Persistent pain or discomfort in your legs
- Significant swelling or skin discoloration
- Open sores or ulcers around the ankles
- Sudden swelling, which may indicate a blood clot
Early treatment of varicose veins can prevent further complications and improve your quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Can varicose veins go away on their own?
No, varicose veins do not go away on their own. While some symptoms may improve with lifestyle changes, such as exercise and weight loss, the veins themselves will not disappear without medical treatment.
2. What causes varicose veins?
Varicose veins are caused by faulty valves in the veins that allow blood to pool, leading to swollen and twisted veins. Risk factors include aging, family history, obesity, pregnancy, and prolonged standing or sitting.
3. Are varicose veins dangerous?
Varicose veins are not typically dangerous, but they can lead to complications such as blood clots, skin ulcers, and chronic venous insufficiency if left untreated.
4. How are varicose veins treated?
Treatment options include lifestyle changes (such as exercise and compression stockings), minimally invasive procedures (like sclerotherapy or laser therapy), and surgical interventions in more severe cases.
5. Can exercise help with varicose veins?
Yes, regular exercise can improve circulation and help manage symptoms of varicose veins. Walking, swimming, and cycling are particularly beneficial.
6. Are varicose veins hereditary?
Yes, varicose veins often run in families. If your parents or grandparents have varicose veins, you are more likely to develop them. A perfect Solution Of Varicose Veins Click Here



