Acute Symptoms of Varicose Veins: Detailed Guide
Varicose veins are enlarged, twisted veins that are commonly found in the legs and feet. These veins often appear blue or dark purple and can be unsightly. While many people associate varicose veins with cosmetic concerns, they can sometimes cause significant discomfort or lead to more severe health issues. When varicose veins become symptomatic, they can cause a range of acute symptoms that may interfere with daily life.
In this guide, we’ll dive into the acute symptoms of varicose veins, potential complications, and how to manage these symptoms effectively.
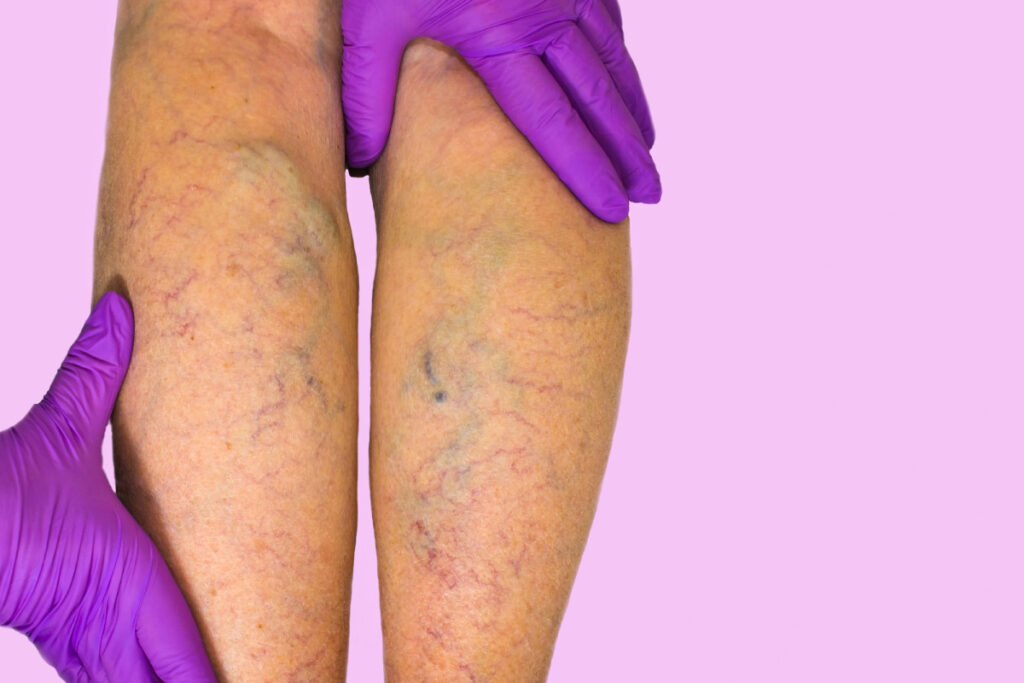
What Are Varicose Veins?
Before we explore the acute symptoms, it’s important to understand what varicose veins are. Varicose veins develop when the valves in the veins weaken, causing blood to pool and veins to enlarge. The legs are most often affected because standing and walking increase the pressure in the veins of the lower body.
Key causes of varicose veins include:
- Genetics (a family history of varicose veins)
- Obesity
- Pregnancy
- Prolonged standing or sitting
- Hormonal changes, such as during menopause
Acute Symptoms of Varicose Veins
While some people with varicose veins experience no symptoms, others may experience discomfort or more severe problems. Here are some of the acute symptoms that may arise:
1. Pain or Aching in the Affected Area
One of the most common acute symptoms of varicose veins is a dull aching or pain, particularly after prolonged periods of standing or sitting. The discomfort is usually localized in the areas where the veins are most prominent, typically in the calves or thighs.
The pain can be described as:
- A burning sensation
- Throbbing in the legs
- Heaviness or tiredness in the legs
The pain may worsen towards the end of the day, especially if you’ve been on your feet for a long time.
2. Swelling in the Legs
Swelling (edema) in the legs and ankles is another acute symptom, as varicose veins interfere with proper circulation. This fluid build-up can cause the legs to feel heavy, tight, and uncomfortable. In some cases, the swelling may extend from the calves down to the ankles and feet.
3. Itching Around the Veins
Itching, also known as venous eczema or stasis dermatitis, is a common but often overlooked symptom of varicose veins. It occurs when poor circulation leads to dry skin and irritation around the affected veins. This itching can become intense and may lead to scratching, which increases the risk of skin infections.
4. Cramping or Muscle Spasms
Many individuals with varicose veins experience cramps or spasms in their legs, especially at night. These cramps can be painful and disruptive, interfering with sleep. They are often caused by poor blood flow and the pressure exerted by enlarged veins.
5. Skin Discoloration
In more advanced cases, varicose veins can lead to changes in skin color, especially around the ankles. The skin may become red, brown, or bluish due to the accumulation of blood and inflammation in the surrounding tissues. This discoloration is often a sign of chronic venous insufficiency and should be addressed by a healthcare professional.
6. Visible Changes in Veins
The most apparent symptom of varicose veins is the visible appearance of bulging, twisted veins just under the surface of the skin. These veins may appear bluish, greenish, or purple and can become more pronounced over time. In some cases, varicose veins may develop into clusters or become harder to the touch.
7. Skin Ulcers
In severe cases, varicose veins can lead to the development of ulcers, particularly around the ankles. These ulcers form when blood flow is severely restricted, leading to skin breakdown. Venous ulcers are slow to heal and can be prone to infection, which may require medical treatment.
8. Bleeding and Bruising
The skin covering varicose veins tends to be thin and fragile, making it more susceptible to injury. Minor bumps or scratches can lead to bleeding or bruising over the affected veins. In some cases, spontaneous bleeding may occur if the veins are severely weakened or damaged.
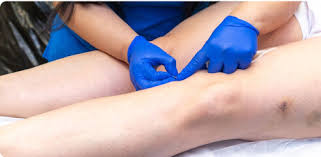
Potential Complications of Acute Varicose Vein Symptoms
When left untreated, acute symptoms of varicose veins can lead to more serious health conditions, including:
1. Thrombophlebitis
Thrombophlebitis refers to the inflammation of a vein caused by a blood clot. In individuals with varicose veins, the blood flow is sluggish, increasing the risk of clot formation. Symptoms include warmth, tenderness, and redness over the affected vein. This condition can be painful and may require medical intervention to prevent further complications.
2. Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
In some cases, blood clots can form in the deep veins, a condition known as deep vein thrombosis (DVT). DVT is a serious condition that requires immediate medical attention, as the clot can travel to the lungs and cause a life-threatening pulmonary embolism. Symptoms of DVT include swelling, warmth, and significant pain in the affected leg.
3. Chronic Venous Insufficiency (CVI)
Chronic venous insufficiency is a long-term condition where the veins cannot pump blood efficiently back to the heart. This can lead to chronic swelling, skin changes, and the formation of ulcers.
Management and Treatment of Acute Symptoms
To manage the acute symptoms of varicose veins, consider the following approaches:
1. Lifestyle Changes
Making certain lifestyle changes can help alleviate discomfort and prevent the worsening of varicose veins:
- Exercise regularly to promote healthy blood circulation.
- Elevate your legs above the heart level several times a day to reduce swelling.
- Avoid prolonged sitting or standing, and take breaks to move around if necessary.
- Wear compression stockings, which can help reduce swelling and pain by improving circulation.
2. Medical Treatments
If lifestyle changes don’t provide relief, medical treatments may be necessary:
- Sclerotherapy: A minimally invasive procedure where a solution is injected into the varicose veins, causing them to collapse and fade over time.
- Laser treatments: This procedure uses laser energy to close off smaller varicose veins.
- Vein stripping and ligation: A more invasive surgical option where large varicose veins are removed.
3. Pain Management
Over-the-counter pain medications such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can be used to manage pain associated with varicose veins. Additionally, cold compresses may help reduce swelling and discomfort.
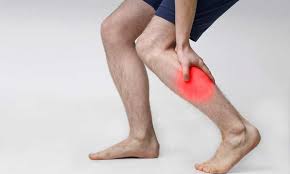
FAQs About Varicose Veins
1. Can varicose veins lead to serious complications? Yes, untreated varicose veins can result in complications such as thrombophlebitis, deep vein thrombosis, and chronic venous insufficiency.
2. Are varicose veins a sign of poor circulation? Yes, varicose veins indicate that blood is not flowing efficiently through the veins, leading to pooling and vein enlargement.
3. Can varicose veins go away on their own? No, varicose veins do not go away on their own. However, lifestyle changes and treatments can help manage symptoms and prevent worsening.
4. How are varicose veins diagnosed? A doctor may use a physical exam and, in some cases, an ultrasound to assess the severity of varicose veins and check for complications.
5. Are there non-surgical treatments for varicose veins? Yes, non-surgical treatments such as sclerotherapy and laser treatments are effective options for treating varicose veins.
6. Can exercise help prevent varicose veins? Yes, regular exercise promotes healthy blood circulation and can help prevent the development or worsening of varicose veins.
A perfect Solution Of Varicose Veins Click Here



