Venous Varicosities: Understanding and Managing Varicose Veins
Venous varicosities, commonly known as varicose veins, are enlarged, swollen, and twisted veins that often appear on the legs and feet. These veins result from poor circulation and weakened valves in the veins, leading to blood pooling in certain areas. While varicose veins are primarily a cosmetic concern for some, they can also cause pain, discomfort, and even lead to more serious health complications if left untreated.
In this article, we will explore the causes of venous varicosities, their symptoms, treatment options, and how to prevent their progression.
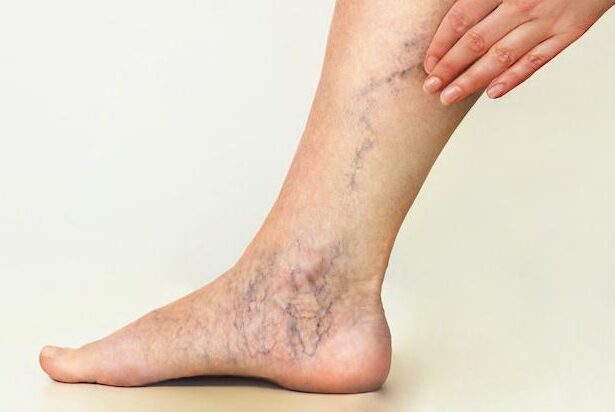
1. What Are Venous Varicosities (Varicose Veins)?
Venous varicosities refer to veins that have become enlarged and twisted due to faulty valves that no longer function properly. Normally, veins carry blood back to the heart, with the help of valves that prevent blood from flowing backward. When these valves weaken, blood can pool in the veins, causing them to stretch and become varicose. The most commonly affected veins are the superficial veins in the legs and feet, as they are subjected to the most pressure from standing and walking.
Common Symptoms of Venous Varicosities:
- Visible, twisted, and bulging veins, often blue or purple in color
- A feeling of heaviness or aching in the legs
- Swelling in the ankles and feet
- Itching around the affected veins
- Skin discoloration or ulcers in severe cases
2. Causes and Risk Factors
Venous varicosities develop due to weakened valves within the veins, but several factors can increase the likelihood of their occurrence. Understanding these risk factors can help in preventing or managing varicose veins more effectively.
Common Causes and Risk Factors:
- Age: As you age, your veins lose elasticity, and valves weaken, increasing the likelihood of varicose veins.
- Genetics: A family history of varicose veins increases your risk.
- Gender: Women are more prone to varicose veins due to hormonal changes during pregnancy, menstruation, and menopause.
- Pregnancy: The increased blood volume during pregnancy can enlarge veins, while hormonal changes relax vein walls.
- Obesity: Excess weight adds pressure to veins, particularly in the legs.
- Prolonged Standing or Sitting: Jobs that require long periods of standing or sitting can reduce circulation and contribute to vein issues.
- Lack of Physical Activity: Sedentary lifestyles can lead to poor circulation, increasing the risk of varicose veins.
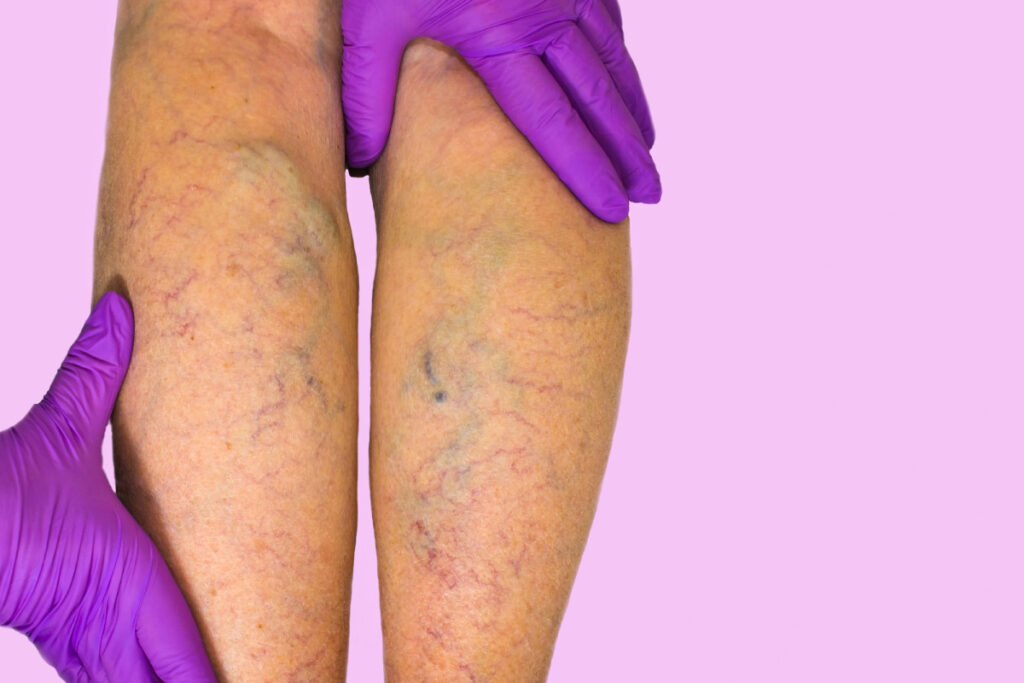
3. How Venous Varicosities Affect the Body
Though venous varicosities are often considered a cosmetic concern, they can cause physical discomfort and even lead to serious complications if untreated. Blood pooling in varicose veins can cause inflammation, swelling, and in some cases, damage to the skin or ulcers. Additionally, varicose veins can signal deeper circulatory issues, such as chronic venous insufficiency.
Complications of Untreated Varicose Veins:
- Venous Ulcers: Open sores near varicose veins, typically around the ankles, which can be slow to heal and prone to infection.
- Blood Clots (Deep Vein Thrombosis): In rare cases, varicose veins can lead to blood clots, causing a more severe condition known as deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
- Bleeding: Superficial varicose veins can sometimes rupture, causing minor bleeding.
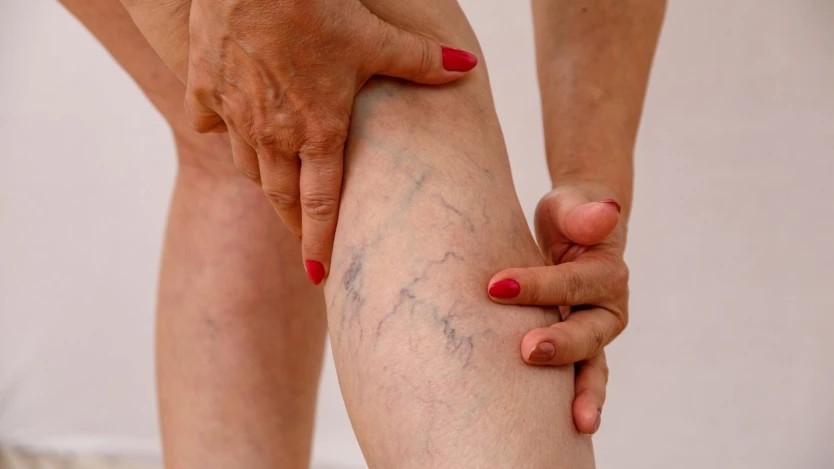
4. Diagnosis of Venous Varicosities
A healthcare provider can diagnose varicose veins by performing a physical examination and asking about symptoms. In some cases, diagnostic tests such as an ultrasound may be ordered to check for more serious complications, like blood clots or deep vein involvement. Ultrasound helps to assess the function of the valves in the veins and the direction of blood flow.
5. Treatment Options for Venous Varicosities
There are several treatments available for managing and treating venous varicosities, ranging from lifestyle changes to medical procedures, depending on the severity of the condition.
a) Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Lifestyle modifications can significantly reduce the discomfort associated with venous varicosities and prevent them from worsening.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity, particularly low-impact exercises such as walking, swimming, or cycling, can improve circulation and strengthen leg muscles, helping to prevent blood from pooling.
- Compression Stockings: Wearing compression stockings helps apply pressure to the legs, promoting better blood flow and reducing swelling.
- Elevating the Legs: Elevating your legs above heart level several times a day can help reduce swelling and improve circulation.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the strain on your legs and lowers the risk of developing varicose veins.
- Avoid Prolonged Sitting or Standing: Changing positions frequently throughout the day can improve circulation and prevent blood from pooling.
b) Medical Treatments
For more severe cases, medical treatments may be required to relieve symptoms and prevent complications.
- Sclerotherapy: This procedure involves injecting a solution into the varicose vein, causing it to collapse and eventually fade away as blood is rerouted through healthier veins. Sclerotherapy is commonly used for smaller veins and spider veins.
- Laser Therapy: Laser treatments use intense bursts of light to close off smaller varicose veins. Over time, the treated veins fade and disappear.
- Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA): This minimally invasive procedure involves inserting a catheter into the affected vein and using radiofrequency energy to heat and seal the vein shut. The blood is then rerouted through healthier veins.
- Endovenous Laser Treatment (EVLT): Similar to RFA, EVLT uses laser energy to close off varicose veins through a small catheter inserted into the vein.
- Vein Stripping and Ligation: In more severe cases, surgical removal of the affected vein may be necessary. This is typically done for larger veins that cannot be treated with less invasive methods.
6. Prevention of Venous Varicosities
Although not all varicose veins can be prevented, there are several strategies to reduce the risk of developing new ones or preventing existing veins from worsening.
Tips for Preventing Venous Varicosities:
- Exercise Regularly: Engaging in physical activity promotes healthy circulation and helps maintain a healthy weight.
- Wear Compression Stockings: Especially if you are prone to varicose veins, compression stockings can help support proper blood flow.
- Avoid Prolonged Standing or Sitting: If you must sit or stand for long periods, make a point to move around or flex your legs frequently to encourage circulation.
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: A diet rich in fiber and low in salt can prevent constipation and reduce swelling, which can lessen the strain on veins.
- Elevate Your Legs: Elevating your legs during rest can help reduce pressure on your veins and improve blood flow.
FAQs
1. Are venous varicosities and varicose veins the same?
Yes, venous varicosities is another term for varicose veins. Both terms refer to veins that have become swollen, twisted, and enlarged due to poor circulation.
2. Can venous varicosities be cured?
While varicose veins can’t be entirely cured without medical intervention, treatments like sclerotherapy, laser therapy, or surgery can remove or close off problematic veins. Lifestyle changes can help manage symptoms and prevent the condition from worsening.
3. Are varicose veins dangerous?
Varicose veins are not usually dangerous but can cause discomfort. In severe cases, complications such as ulcers, blood clots, or bleeding can occur. Consult a doctor if your symptoms worsen.
4. Can compression stockings eliminate varicose veins?
Compression stockings won’t eliminate varicose veins, but they can help reduce swelling, pain, and discomfort by improving circulation and preventing blood from pooling.
5. Do varicose veins require surgery?
Surgery is typically reserved for more severe cases where less invasive treatments are ineffective. Many people with varicose veins can manage their symptoms with lifestyle changes and non-invasive procedures.
6. Can pregnancy cause varicose veins?
Yes, pregnancy increases the risk of developing varicose veins due to the increase in blood volume and hormonal changes that relax vein walls. They often improve after pregnancy, but treatment may be needed if they persist.
Conclusion
Venous varicosities, or varicose veins, are a common condition that can cause discomfort and lead to more serious complications if untreated. While lifestyle changes can help manage symptoms, medical treatments are often required to address more severe cases. By taking proactive steps such as exercising regularly, wearing compression stockings, and maintaining a healthy diet, you can reduce your risk of developing varicose veins or prevent them from worsening.
A Product That Help in Varicose Veins Is Varicosure



