Are Varicose Vein Symptoms Easily Diagnosable? Causes, Symptoms, and Diagnostic Methods
Varicose veins, often recognized as swollen and twisted veins, usually affect the legs and are a common condition, especially among adults. While many people see varicose veins as primarily a cosmetic issue, they can lead to discomfort and sometimes severe complications if left untreated. Identifying and diagnosing varicose veins early can help manage symptoms and prevent complications. Are Varicose Vein Symptoms Easily Diagnosable.
In this article, we’ll explore how varicose vein symptoms are typically diagnosed, what the common symptoms are, and when you should seek medical advice for this condition. Understanding the diagnostic process will help you take the necessary steps toward treatment and symptom management.
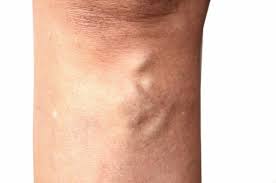
What Are Varicose Veins?
Varicose veins develop when the veins’ valves, which help direct blood flow toward the heart, become weak or damaged. This results in blood pooling in the veins, causing them to enlarge, twist, and bulge visibly beneath the skin. Varicose veins commonly appear in the legs and feet because standing and walking increase pressure in the veins of the lower body.
While varicose veins can sometimes be purely a cosmetic concern, they can also cause discomfort and lead to more serious health issues like skin ulcers or blood clots. Early diagnosis and management are essential for preventing complications.
Common Symptoms of Varicose Veins
Recognizing the symptoms of varicose veins is crucial for early diagnosis. Symptoms can range from mild to severe, and they often worsen over time if not treated. Here are the common symptoms to look out for:
1. Visible Swollen, Twisted Veins
The most recognizable symptom of varicose veins is the appearance of bulging, twisted, or swollen veins, often blue or purple in color, that are visible just under the skin. These veins are typically located in the legs but can also appear in other parts of the body.
2. Aching or Throbbing Pain
Many people with varicose veins experience a dull aching or throbbing pain in their legs, especially after standing or sitting for extended periods. The pain often worsens as the day progresses and may be accompanied by a feeling of heaviness in the legs.
3. Swelling in the Lower Legs and Ankles
Swelling, particularly in the lower legs and ankles, is another common symptom. The swelling is often more pronounced at the end of the day and may decrease after resting or elevating the legs.
4. Heaviness or Fatigue in the Legs
A feeling of heaviness or tiredness in the legs is frequently reported by individuals with varicose veins. This symptom can make standing or walking for long periods uncomfortable and may interfere with daily activities.
5. Itching or Irritation
Itching or irritation around the affected veins is another common symptom. This may be a sign of skin changes related to the varicose veins and can sometimes lead to more serious skin issues, such as venous ulcers.
6. Muscle Cramps and Restless Legs
Nighttime muscle cramps or restless legs syndrome (RLS) is often associated with varicose veins. These symptoms can disrupt sleep and contribute to further discomfort during the day.
7. Skin Changes
In more advanced cases, the skin around varicose veins may become discolored, hardened, or develop sores (venous ulcers). These changes usually indicate chronic venous insufficiency (CVI), a more serious condition that occurs when varicose veins are left untreated.
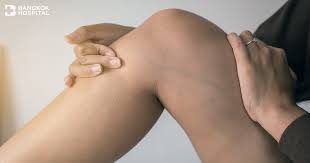
Are Varicose Vein Symptoms Easily Diagnosable?
Yes, varicose vein symptoms are generally easy to diagnose, especially based on their physical appearance and the associated discomfort. However, a proper diagnosis is essential to determine the severity of the condition and to rule out other potential health issues. A healthcare professional will typically use a combination of physical examinations and diagnostic tools to assess the condition accurately.
1. Physical Examination
The most common method of diagnosing varicose veins involves a simple physical examination. During the exam, a healthcare provider will visually inspect the legs for swollen, twisted veins and may palpate the area to assess pain, tenderness, or swelling. In many cases, the diagnosis can be made based on this visual inspection alone.
2. Patient History
A detailed medical history is also important in diagnosing varicose veins. Your doctor may ask about your symptoms, when they started, whether they worsen at certain times (like after prolonged standing), and whether you have a family history of varicose veins or other vein-related conditions.
3. Doppler Ultrasound
For a more detailed evaluation, your healthcare provider may recommend a Doppler ultrasound. This non-invasive test uses sound waves to visualize the blood flow in the veins and detect any abnormalities, such as valve malfunctions or blood clots. The ultrasound helps determine whether the veins are functioning properly and whether the blood is pooling in the affected veins.
4. Venogram (Rarely Used)
In rare cases, a venogram might be used to assess the condition of the veins. This test involves injecting a special dye into the veins and taking X-rays to see how blood flows through them. However, it’s generally not necessary for diagnosing varicose veins and is typically reserved for more complex cases.
When to Seek Medical Attention for Varicose Veins
While mild varicose veins may not require immediate medical attention, it’s important to seek professional help if you experience any of the following:
- Persistent pain, aching, or swelling in the legs
- Skin changes, such as discoloration or thickening near the veins
- Open sores or ulcers near the affected veins
- Bleeding from varicose veins, which may occur after a minor injury
- Symptoms of a blood clot, such as sudden leg swelling, warmth, and redness
Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent these complications and improve your quality of life.
Treatment Options for Varicose Veins
Once varicose veins have been diagnosed, there are several treatment options available. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of the condition and your symptoms. Common treatments include:
1. Lifestyle Changes
For mild cases, lifestyle changes can help manage symptoms and prevent the condition from worsening. These include:
- Regular exercise to improve circulation
- Elevating the legs to reduce swelling
- Avoiding prolonged standing or sitting
- Wearing compression stockings to promote blood flow
2. Minimally Invasive Treatments
For more severe cases, medical treatments may be necessary to remove or close off the varicose veins. These treatments include:
- Sclerotherapy: A solution is injected into the varicose veins, causing them to collapse and fade over time.
- Laser Therapy: Laser energy is used to close off smaller varicose veins.
- Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA): Heat is used to seal off the affected veins.
- Endovenous Laser Therapy (EVLT): A laser fiber is inserted into the vein, heating and sealing it from the inside.
3. Surgical Options
In cases where the varicose veins are large or causing significant discomfort, surgery may be required. Options include:
- Vein Stripping and Ligation: The affected veins are surgically removed or tied off.
- Phlebectomy: Small incisions are made to remove superficial varicose veins.
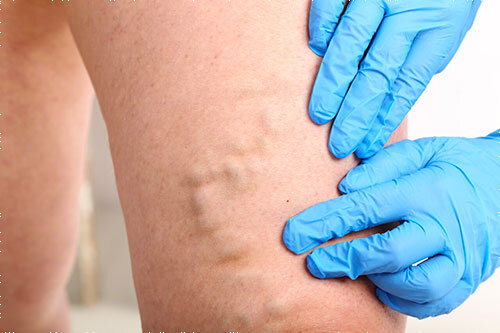
FAQs About Diagnosing Varicose Veins
1. Can varicose veins be diagnosed without a doctor?
While you can often recognize varicose veins by their appearance and symptoms, it’s important to get a formal diagnosis from a healthcare professional. A doctor can determine the severity of the condition and recommend appropriate treatments.
2. What tests are used to diagnose varicose veins?
The most common test is a physical examination, but a Doppler ultrasound may also be used to assess blood flow in the veins. In rare cases, a venogram might be required for more complex conditions.
3. Is varicose vein diagnosis painful?
No, the diagnostic process for varicose veins is generally not painful. A physical examination and Doppler ultrasound are non-invasive and involve minimal discomfort.
4. Can varicose veins lead to other health problems if left untreated?
Yes, untreated varicose veins can lead to complications such as chronic venous insufficiency, skin ulcers, blood clots, and increased risk of deep vein thrombosis (DVT). Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent these issues.
5. How do I know if my varicose veins are serious?
If you experience significant pain, swelling, skin changes, or open sores near the affected veins, it’s a sign that the condition may be serious. You should seek medical attention if these symptoms occur.
6. What is the best treatment for varicose veins?
The best treatment depends on the severity of your varicose veins. Mild cases may respond well to lifestyle changes and compression stockings, while more severe cases may require minimally invasive procedures or surgery.
A Product That Help in Varicose Veins Is Varicosure



